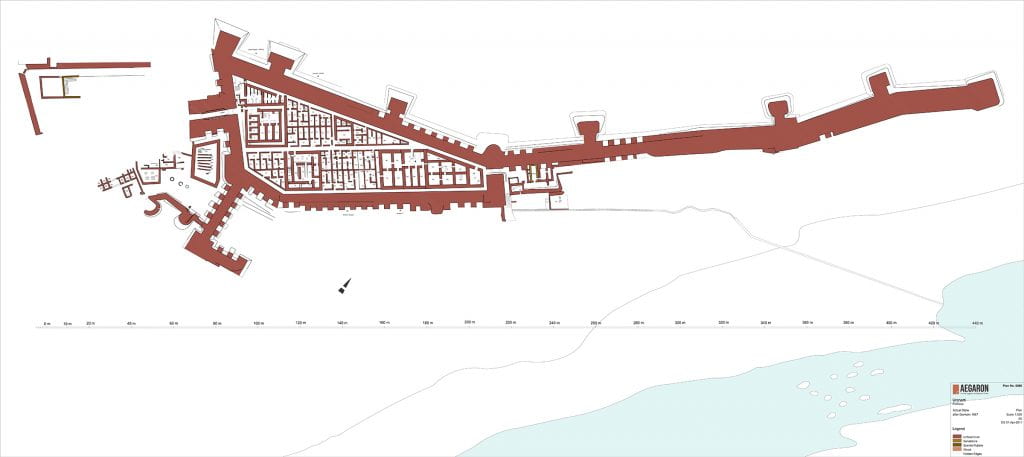
Uronarti plan, fortress, actual state, no. 0086 (after Dunham 1967), drawing by AEGARON, http://drupaldev.aegaron.ucla.edu/drawing/21198_zz002ch0q7
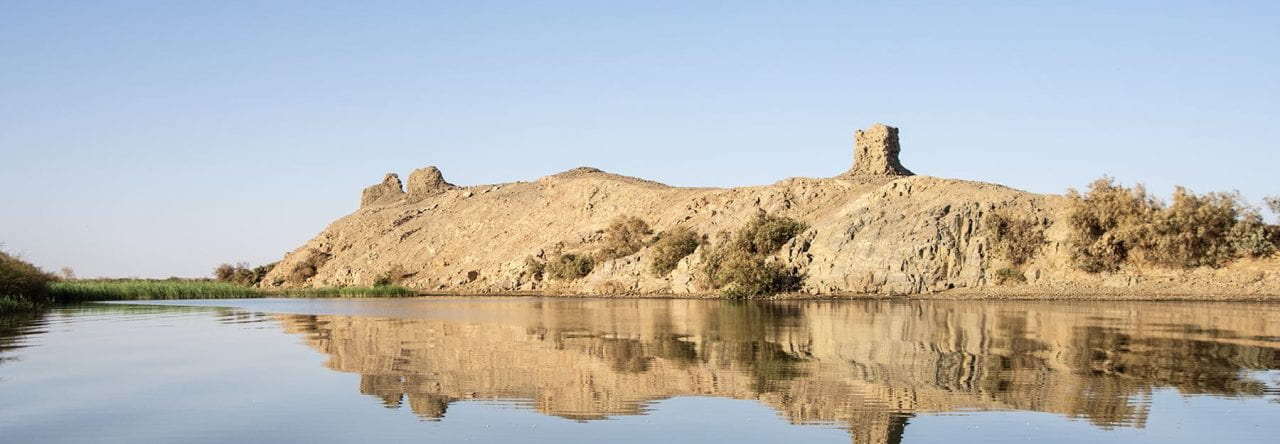
Uronarti is one of the southern group of fortresses built in the Middle Kingdom in the region of the Second Cataract. Like many of the southern forts, Uronarti’s shape conforms to the rocky landscape in which it was built. Its main area is approximately 140m (460 feet) long, with outer walls measuring 5m (16 feet) thick. We think they would originally have been about 10m tall (32 feet) but only small portions remain standing. Many of the bricks were removed by farmers to spread on their fields in the last centuries because they are good dirt for agriculture in this barren area. A northern extension of the outer wall sticks out like a spur for another 220m (720 feet), not enclosing anything but making it impossible for anyone to cross the island at that point and allowing for lookout posts.
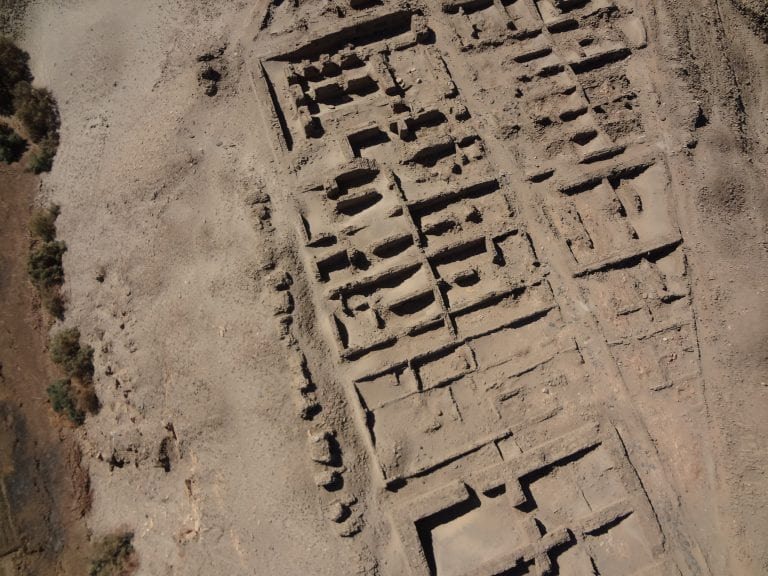

The middle part of Uronarti fort from a kite photo. The thick-walled treasury is at the bottom, the possible governor’s house at the top, and barracks cover most of the area shown.
The main entrance, a fortified gateway, is on the south. It would have been difficult to storm – the slope leading up to it is very steep. The interior of the fort is entirely built up, with no open spaces. It contains large buildings with thick walls in both the north and south, and thinner-walled structures in many areas. The northern-most interior buildings are square and conform to our expectations of Middle Kingdom granaries. In the south are administrative and residential buildings for the most important people in the fortress. The thinner-walled structures appear to have been barracks. A network of streets ran along the insides of the main fort walls and between blocks of buildings, allowing easy movement between parts of the fortress. The main street, down the center of the fort, was lined with rough slabs of the local stone.
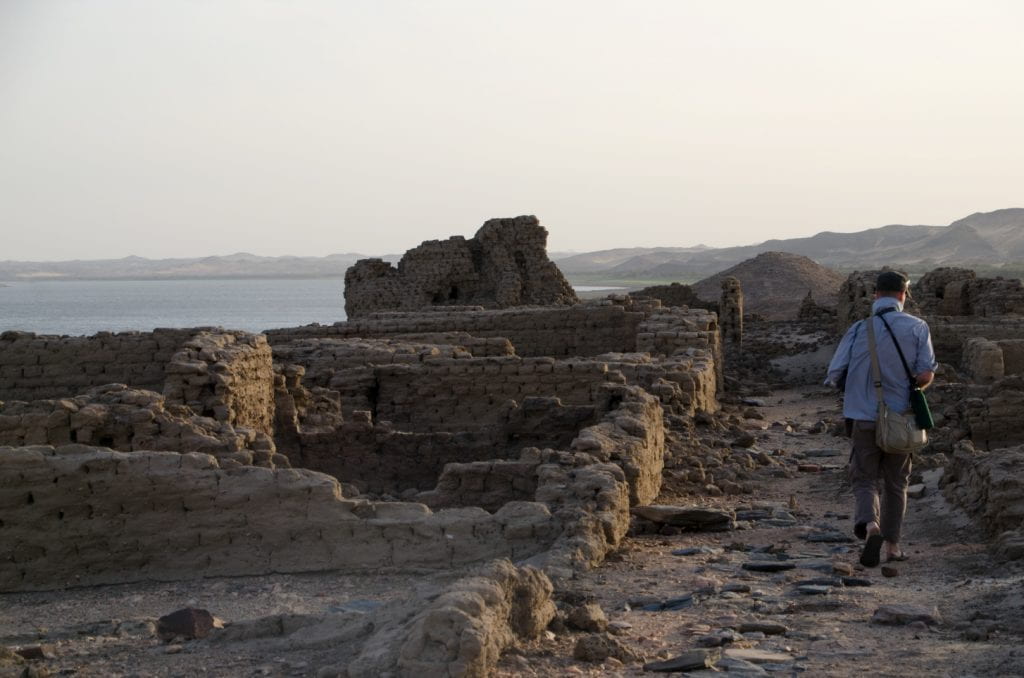

Walking down the main street of Uronarti. Originally cleared by Wheeler in 1928-30, the street has never been covered again. Erosion is a bigger concern than deposition at Uronarti.
Getting water would always have been a difficult part of life at Uronarti, as indeed it is for those of us who work there now. A set of stairs, partly constructed and partly hewn out of the rock, originally led down from the fortress under the protection of the northern spur wall. Lower portions of the stairs were roofed, giving added protection. The stairs are now almost entirely missing, with the rise in the water covering their bottom portions and their top sections eroded thanks to being on the very steepest part of the rock spur.

The lower portion of the river stairs, looking north. This is now permanently below water. Dunham 1967, Plate XII.B.
We originally thought to put our camp inside the fortress itself – the preservation of the walls is high enough to serve as a block on the wind, and we would have been so convenient to work! But the trouble of getting water quickly dissuaded us.
Thinking about how water was fetched, the hard, hot slog back up to the fortress with heavy pots happening day in and day out, reminds us to ask questions about what life was actually like at Uronarti. Teasing out the construction history of the fortress is a way we can do this archaeologically, and is one of the main current projects of the URAP.

Different brick recipes can be a clue to phasing. Darker, siltier bricks are lower than sandy, yellower bricks in this remodeled wall.
It is clear that construction was much more complicated than just a state blueprint leading in one fell swoop to the complete plan we see today. In the first place, the fortress was built so that the floor level was the same in all buildings, but since the original topography was highly irregular and very steep this meant that a great deal of terracing had to happen even before the first buildings could be built. One function of the massive outer walls was to retain sand and rubble that were used to raise the sides of the site to their intended height. Even the interior walls of the fortress speak to this need: the plans of rooms are evident well below floor level and multiple episodes of filling are evident. Even in the extant above-ground architecture we have evidence of at least two major phases. We can see this because the recipe for the bricks changed. The outer walls and the walls of the main interior buildings were built entirely in a silty brown type of brick, but modifications of these walls, as well as the initial construction of some of the barracks, utilized a much sandier, yellow, brick. It is possible that the brick differences are due to different places of manufacture or to manufacture at different times of year. Whatever the cause, the recipe change is a helpful – though incomplete – index to phasing for us.
Beyond being able to see that even the first buildings at Uronarti were built over time, we can see modifications and remodeling everywhere we look. Some of this was simply necessary to keep the buildings from falling down – mudbrick requires constant maintenance – but some appears to relate to both minor and major rethinking of how structures functioned. Rooms that had been free acquired bins and troughs for animal feeding, built out of brick. Doors were filled or cut. Three-room houses were expanded into adjacent originally similar buildings, perhaps as the social structures of the inhabiting population changed – male garrisons to families? Unfortunately, Wheeler’s quick and dirty excavations did not record the stratigraphy within the fortress, nor in most cases was he interested in anything other than the original plan of the fort, so he ripped out later walls. This is one of the areas of chief interest to us, however, and enough remains to make it a fruitful avenue of research.
So far, we have approached architectural modification through excavation and careful recording of walls, comparing what we have left with what Wheeler noted in those cases when he took note of removing later walls. The results are already illuminating. Substantial intact strata beneath the thick-walled buildings in the south show us the complicated process of construction in which the landscape was terraced, retaining walls were built, and leveling fills of sand were brought in. While this was happening, cooking fires in places that would become formal buildings suggest the camps of building crews.

Sub-floor stratigraphy in Unit FA, the southwestern room of the fortress. All of the visible strata date to the original construction of the fortress, as evidenced by the ceramics in the rubble fill that was deposited as part of the massive terracing efforts needed to level the site.
While all of the barracks seem to have been laid out in plan from the beginning, with a single course of bricks showing where walls were to be built, it appears that the actual construction of those houses may have started in the south and not initially filled the entire empty space. By the time houses were built in the north, layouts were much more idiosyncratic.
In later phases, the system of streets was heavily compromised, with animal pens and even more major constructions blocking off access in nearly every street. We can imagine the inhabitants of the fortress moving around across rooftops, or through a rabbits’ warren of doors knocked through rooms, but can no longer think that they marched in order down streets. Modifications to garrisons may suggest changing social structures, and certainly indicate that some housing areas were repurposed for storage and administrative activities. Major buildings were heavily modified, too. The remodeling gives us a sense of this place as dynamic – a setting for actual people, living complex lives, changing their surroundings as their needs changed.

Excavating Unit CC in the northern barracks, complicated by a parade of goats.
