PAPERS
The hyphal-specific toxin candidalysin promotes fungal gut commensalism
Nature. 2024. 627(8004):620-627. PMID: 38448595. Liang S-H, Sircaik S, Dainis J, Kakade P, Penumutchu S, McDonough LD, Chen Y-H, Frazer C, Schille TB, Allert S, Elshafee O, Hänel M, Mogavero S, Vaishnava S, Cadwell K, Belenky P, Perez JC, Hube B*, Ene IV, Bennett RJ*.
Filamentation and biofilm formation are regulated by the phase-separation capacity of network transcription factors in Candida albicans.
PLoS Pathogens. 2023. 19(12):e1011833. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011833. Ganser C, Staples MI. Dowell M, Frazer C, Dainis J, Sircaik S and Bennett RJ.
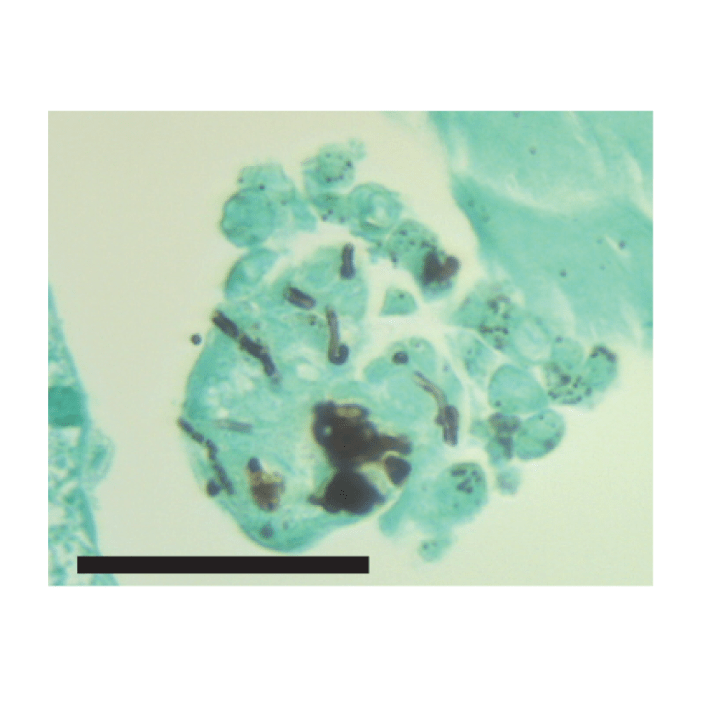
Rewilding of laboratory mice enhances granulopoiesis and immunity through intestinal fungal colonization.
Science Immunology. 2023.
8(84):eadd6910. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.add6910.
Chen YH, Yeung F, Lacey KA, Zaldana K, Lin JD, Bee GCW, McCauley C, Barre RS, Liang S-H, Hansen CB, Downie AE, Tio K, Weiser JN, Torres, VJ, Bennett RJ, Loke P, Graham AL, Cadwell K
Phase separation in fungi
Nature Microbiology. 2023. 8(3): 375-386. doi: 10.1038/s41564-022-01314-6. Staples MI, Frazer C, Fawzi NL, Bennett RJ.
Aneuploidy and gene dosage regulate filamentation and host colonization by Candida albicans.
PNAS. 2023. 120(11) e2218163120. Kakade P, Shabnam S, Maufrais C, Ene IV*, Bennett RJ*.
Ploidy changes in human fungal pathogens: going beyond sexual reproduction.
PLoS Pathogens. 2022. 18(12):e1010954. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010954. Du H, Zheng Q, Bennett RJ, Huang G.
Friendly fungi : symbiosis with commensal Candida albicans.
Trend Immunol. 2022. 43(9):706-717. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2022.07.003. Shao TY, Haslam DB, Bennett RJ*, Way SS*.
An adjuvant-based approach enables the use of dominant HYG and KAN selectable markers in Candida albicans.
mSphere. 2022. 7(4):e0034722. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00347-22. Park S, Frazer C, Bennett RJ*.
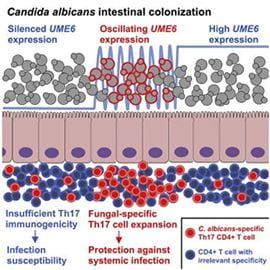
Candida albicans oscillating UME6 expression during intestinal colonization primes systemic Th17 protect immunity.
Cell Reports. 2022. 39(7): 11083. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110837. Shao TY, Kakade P, Witchley JN, Frazer C, Murray KL, Ene IV, Haslam DB, Hagan T, Noble, SM, Bennett RJ, Way SS.
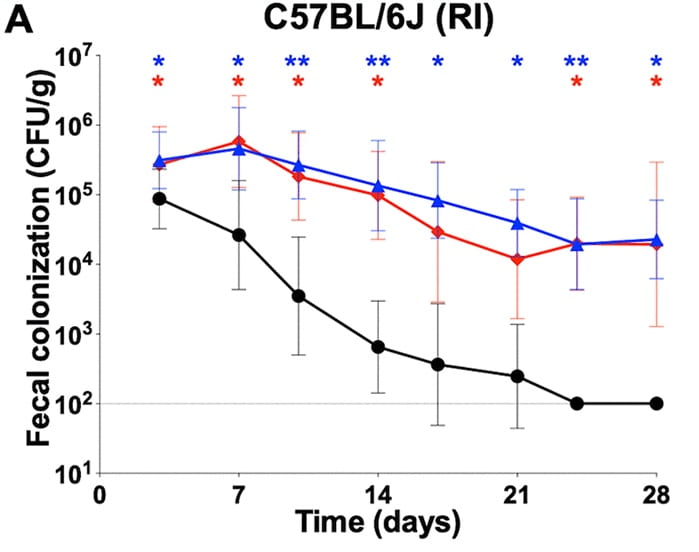
Candida albicans isolates 529L and CHN1 exhibit stable colonization of the murine gastrointestinal tract.
mBio. 2021. 12(6):e0287821. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02878-21. McDonough LD, Mishra AA, Toscini N, Kakade P, Penumutchu S, Liang S-H, Maufrais C, Zhai B, Taur Y, Belenky P, Bennett RJ*, Hohl T*, Koh AY*, Ene IV*.
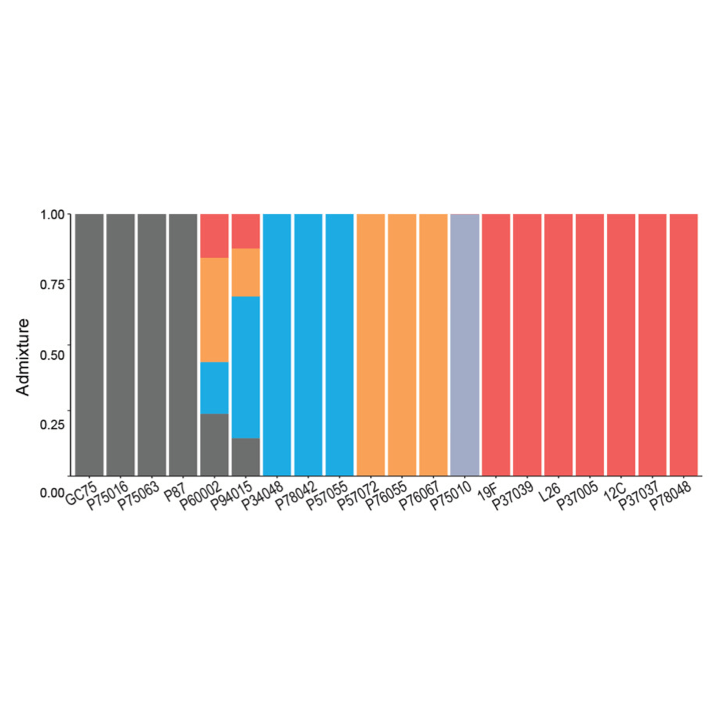
Intraspecies profiling reveals key regulators of Candida albicans pathogenic traits.
mBio. 2021. 12(2):e00586-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00586-21. Wang JM, Woodruff AL, Dunn MJ, Fillinger RJ, Bennett RJ, Anderson AZ.
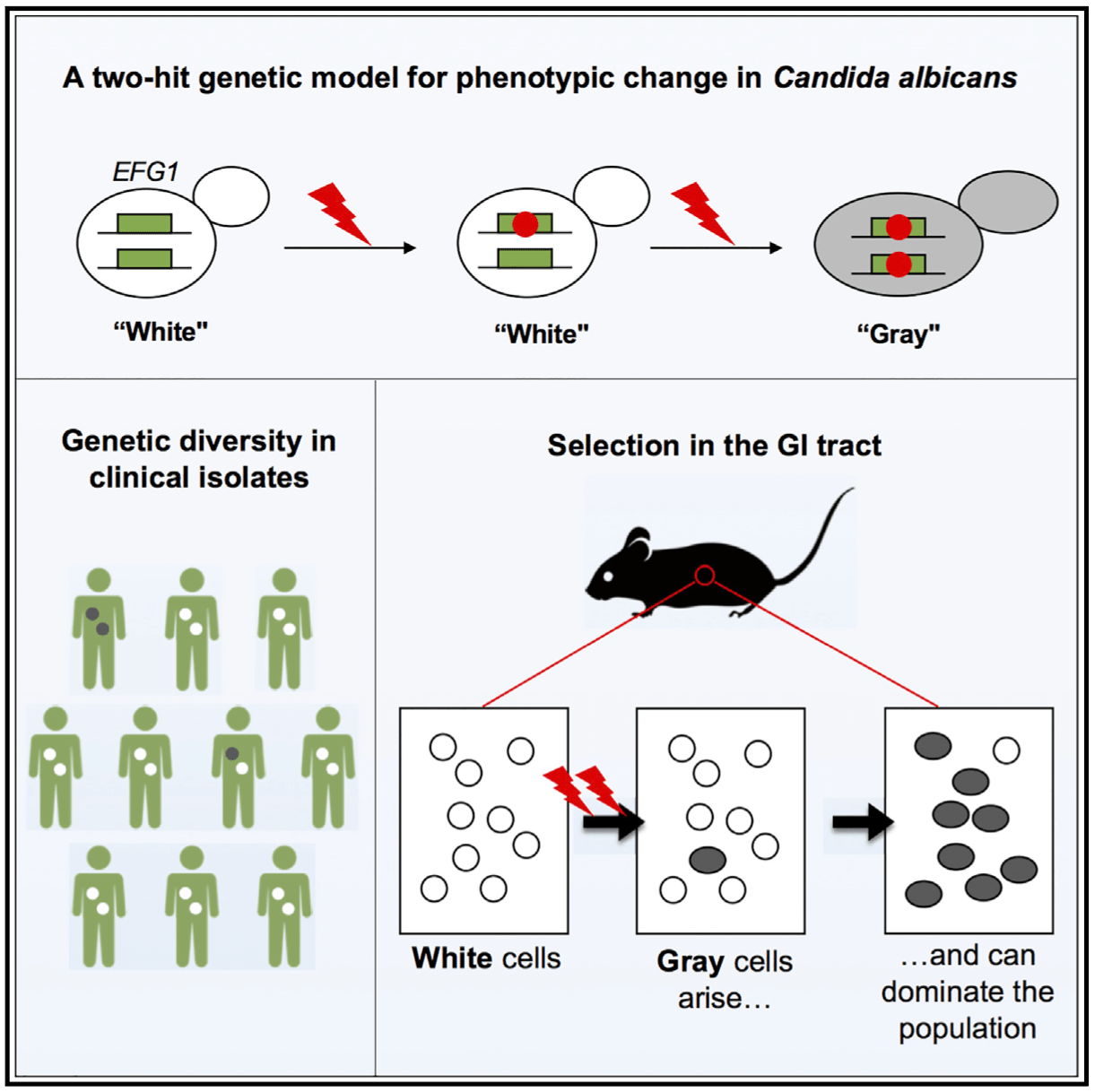
Comparative genomics of white and opaque cell states supports an epigenetic mechanism of phenotypic switching in Candida albicans.
G3 (Bethesda). 2021. 11(2):jkab001. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab001. Beekman CN, Cuomo CA, Bennett RJ, Ene IV.
Adaptation to the dietary sugar D-tagatose via genome instability in polyploid Candida albicans cells
G3 (Bethesda). 2021. 11(7): jkab110. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab110. Thomson GJ, Kakade P, Hirakawa MP, Ene IV, Bennett RJ.
Epigenetic cell fate in Candida albicans is controlled by transcription factor condensates acting at super-enhancer-like elements
Nature Micro. 2020. 5(11):1374-1389. Frazer C, Staples MI, Kim Y, Hirakawa M, Dowell MA, Johnson NV, Hernday AD, Ryan VH, Fawzi NL, Finkelstein IJ, Bennett RJ.
Additional Publications
Hemizygosity enables a mutational transition governing fungal virulence and commensalism.
Cell Host Microbe. 2019 25(3):418-431.e6. Liang SH, Anderson MZ, Hirakawa MP, Wang JM, Frazer C, Alaalm LM, Thomson GJ, Ene IV, Bennett RJ.
Metabolism-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage selectively trigger genome instability in polyploid fungal cells.
EMBO J. 2019. 38(19):e101597. Thomson GJ, Hernon C, Austriaco N, Shapiro RS, Belenky P, Bennett RJ.
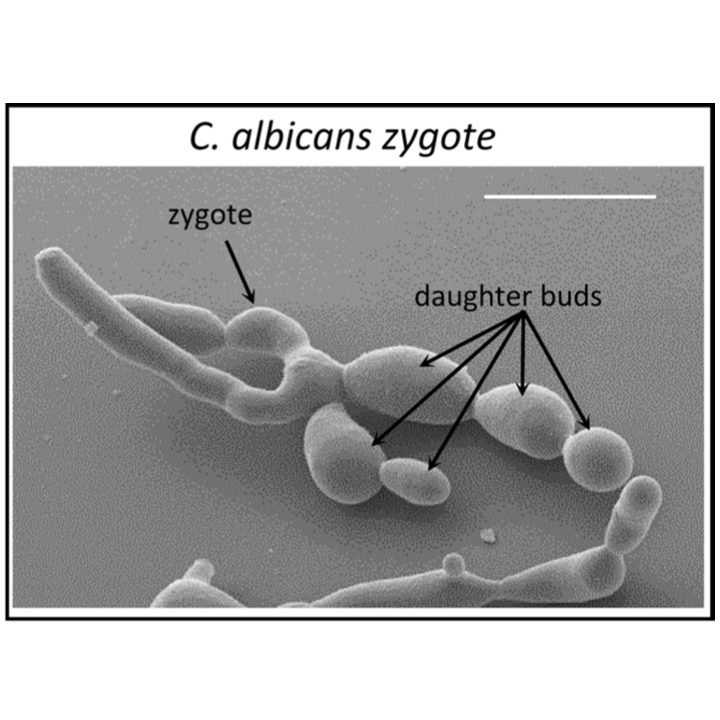
A 'parameiosis' drives depolyploidization and homologous recombination in Candida albicans.
Nature Comm. 2019. 10(1):4388. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12376-2. Anderson MZ, Thomson GJ, Hirakawa MP, Bennett RJ.
The impact of gene dosage and heterozygosity on the diploid pathobiont Candida albicans.
J Fungi (Basel). 2019. 6(1):10. doi: 10.3390/jof6010010. Liang SH, Bennett RJ.
Genetic modification of closely related Candida species.
Front Microbiol. 2019. 10:357. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00357. Mancera E, Frazer C, Porman AM, Ruiz-Castro S, Johnson AD, Bennett RJ.
Monitoring phenotypic switching in Candida albicans and the use of next-gen fluorescence reporters.
Curr Protoc Microbiol. 2019. 53(1):e76. doi: 10.1002/cpmc.76. Frazer C, Hernday AD, Bennett RJ.
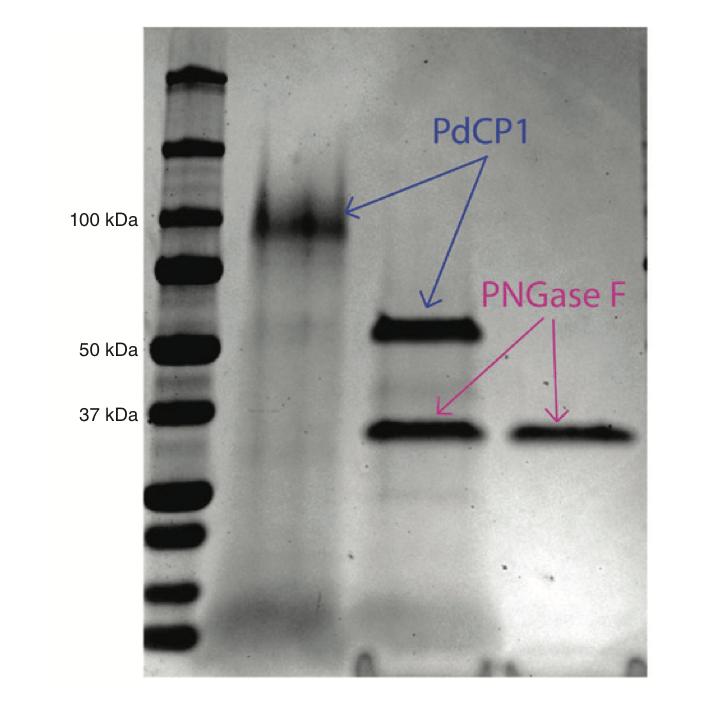
Characterization of PdCP1, a serine carboxypeptidase from Pseudogymnoascus destructans, the causal agent of White-nose Syndrome.
Biol Chem. 2018. 399(12):1375-1388. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2018-0240. Beekman C, Jiang Z, Suzuki BM, Palmer JM, Lindner DL, O’Donoghue AJ, Knudsen GM, Bennett RJ.
Galleria mellonella as an insect model for P. destructans, the cause of White-nose Syndrome in bats
PLoS One. 2018. 13(9):e0201915. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201915. Beekman CN, Meckler L, Kim E, Bennett RJ.
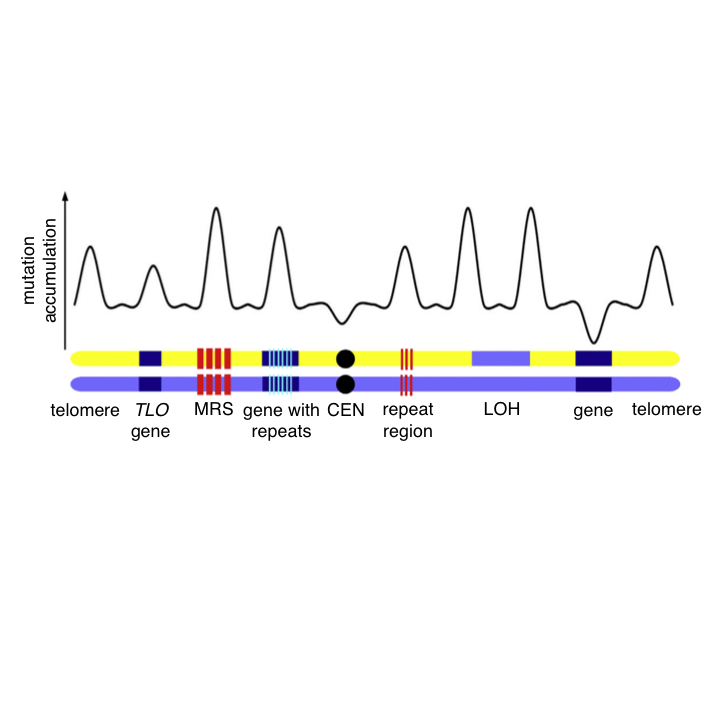
The genome of the human pathogen Candida albicans is shaped by mutation and cryptic sexual recombination.
mBio. 2018. 9(5):e01205-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01205-18. Wang JM, Bennett RJ, Anderson MZ.
Global analysis of mutations driving microevolution of a heterozygous diploid fungal pathogen
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018. 115(37):E8688-E8697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1806002115. Ene IV, Farrer RA, Hirakawa MP, Agwamba K, Cuomo CA, Bennett RJ.
Antifungal tolerance is a subpopulation effect distinct from resistance and is associated with persistent candidemia.
Nat Commun. 2018. 9(1):2470. Rosenberg A, Ene IV, Bibi M, Zakin S, Segal ES, Ziv N, Dahan AM, Colombo AL, Bennett RJ, Berman J.
A coupled process of same- and opposite-sex mating generates polyploidy and genetic diversity in Candida tropicalis.
PLoS Genet. 2018. 14(5):e1007377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007377. Du H, Zheng Q, Bing J, Bennett RJ, Huang G.
Epigenetic control of pheromone MAPK signaling determines sexual fecundity in Candida albicans.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017. 114(52):13780-13785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711141115. Scaduto CM, Kabrawala S, Thomson GJ, Scheving W, Ly A, Anderson MZ, Whiteway M, Bennett RJ.
Parasex generates phenotypic diversity de novo and impacts drug resistance in Candida albicans.
Genetics. 2017. 207(3):1195-1211. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300295. Hirakawa MP, Chyou DE, Huang D, Slan AR, Bennett RJ.
Negative regulation of filamentous growth in Candida albicans by Dig1p.
Mol Microbiol. 2017 Sep;105(5):810-824. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13738. Regan H, Scaduto CM, Hirakawa MP, Gunsalus K, Correia-Mesquita TO, Sun Y, Chen Y, Kumamoto CA, Bennett RJ, Whiteway M.
Negative regulation of filamentous growth in Candida albicans by Dig1p.
Mol Microbiol. 2017 Sep;105(5):810-824. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13738.
Development of a CRISPR-Cas9 System for efficient genome editing of Candida lusitaniae.
mSphere. 2017. 2(3):e00217-17. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00217-17.
A chromosome 4 trisomy contributes to increased fluconazole resistance in a clinical isolate of Candida albicans.
Microbiology. 2017. 163(6):856-865. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000478. Anderson MZ, Saha A, Haseeb A, Bennett RJ.
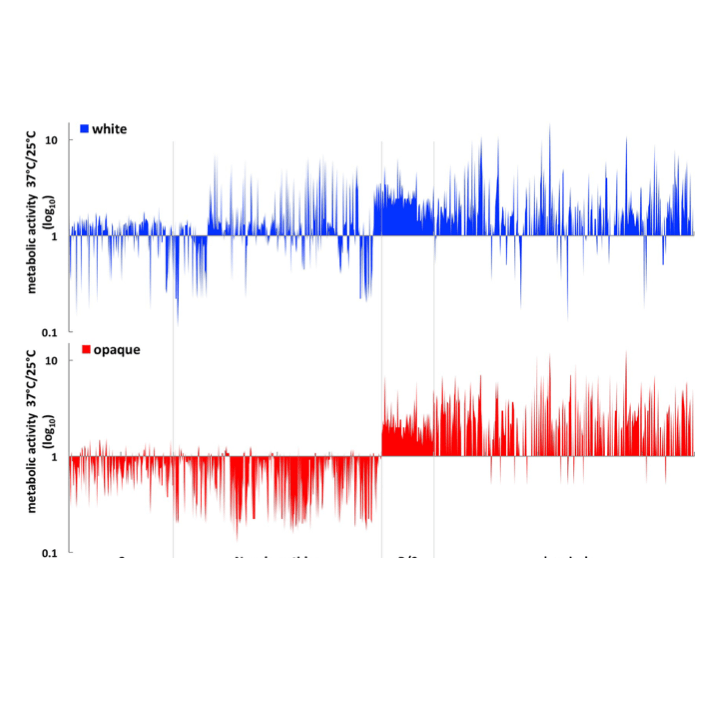
Phenotypic profiling reveals that Candida albicans opaque cells represent a metabolically specialized cell state compared to default white cells.
mBio. 2016. 7(6):e01269-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01269-16.
Fungal Sex: The Ascomycota.
Microbiol Spectr. 2016. Oct;4(5). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0005-2016.
Deletion of a Yci1 domain protein of Candida albicans allows homothallic mating in MTL heterozygous cells.
mBio. 2016. 7(2):e00465-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00465-16. mBio.
Phenotypic profiling reveals that Candida albicans opaque cells represent a metabolically specialized cell state compared to default white cells.
mBio. 2016. 7(6):e01269-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01269-16.
Fungal Sex: The Ascomycota.
Microbiol Spectr. 2016. Oct;4(5). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0005-2016.
Deletion of a Yci1 domain protein of Candida albicans allows homothallic mating in MTL heterozygous cells.
mBio. 2016. 7(2):e00465-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00465-16. mBio.